OAuth2 Authorization Code
The code examples below are C# code without making use of any specific OAuth library.
Authorization Code
The OAuth2 “authorization code flow” has the advantage that the Client Application does not have to store the 2BA user’s credentials. A coupling is established once for each user. This is achieved via the 2BA login page. This process takes the following steps:
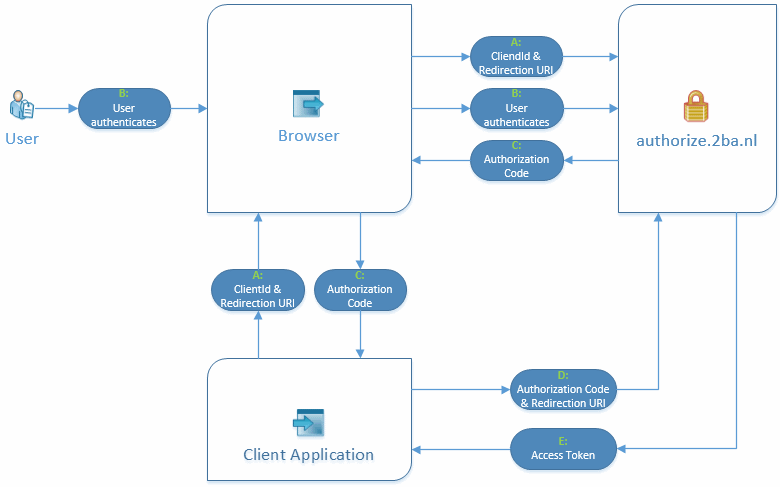
The application opens an (embedded) browser and navigates to the 2BA authorization server (https://authorize.2ba.nl/). This request contains the following parameters
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| response_type=code | Specifies that the authorization server should return an authorization code |
| client_id | Used to identify the client application. A software partner can obtain this by contacting 2BA |
| redirect_uri | The URL to navigate to once the login procedure has completed. The url is required and must be conform the http(s) scheme. (must begin with http(s). e.g. https://www.2ba.nl). The url can also be localhost. (e.g. http://localhost:8080) Note that this URL must be registered under your 2BA ClientId. Please send a mail to us with all needed redirect_uri’s ! |
var url = new Uri(string.Format("{0}/OAuth/Authorize?response_type=code&client_id={1}&redirect_uri={0}",
Properties.Settings.Default.AuthorizeUrl,
Globals.ClientId));
this.WebBrowser1.Navigate(url);
The user enters his/her credentials using the login page
Navigation returns to the URL specified by redirect_uri with the parameter ?code={authorization_code}.
This response can be parsed. For example:
private void WebBrowser1_Navigated(object sender, WebBrowserNavigatedEventArgs e)
{
//Look for the authorization code field
const string SearchCondition = "/?code=";
if (e.Url.PathAndQuery.StartsWith(SearchCondition))
{
var queryString = string.Join(string.Empty, e.Url.AbsoluteUri.Split('?').Skip(1));
var parsedQuery = HttpUtility.ParseQueryString(queryString);
this.Authorization_Code = parsedQuery["code"];
this.DialogResult = DialogResult.OK;
this.Close();
}
}
The token service (see below) is then invoked with a grant_type of “authorization_code” and the ‘code’ parameter set to the autorization code retrieved earlier:
public static OAuthTokenResponse GetAccessToken(string authorizationCode)
{
var postMessage = string.Format("grant_type=authorization_code&code={0}&client_id={2}&client_secret={3}&redirect_uri={1}",
authorizationCode,
Settings.Default.AuthorizeUrl,
Globals.ClientId,
Globals.ClientSecret);
var request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(Settings.Default.AuthorizeUrl + "/OAuth/Token");
var data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(postMessage);
request.Method = "POST";
request.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
request.ContentLength = data.Length;
using (var stream = request.GetRequestStream())
{
stream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}
The token service returns the access_token, refresh_token, lifetime etc. which can then be used to invoke Unifeed or our other services:
var response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse();
var responseString = new StreamReader(response.GetResponseStream()).ReadToEnd();
var token = new OAuthTokenResponse();
var jobj = JObject.Parse(responseString);
token.AccessToken = (string)jobj["access_token"];
token.RefreshToken = (string)jobj["refresh_token"];
token.ExpiresIn = (int)jobj["expires_in"];
token.TokenGet = DateTime.Now;
return token;
}




